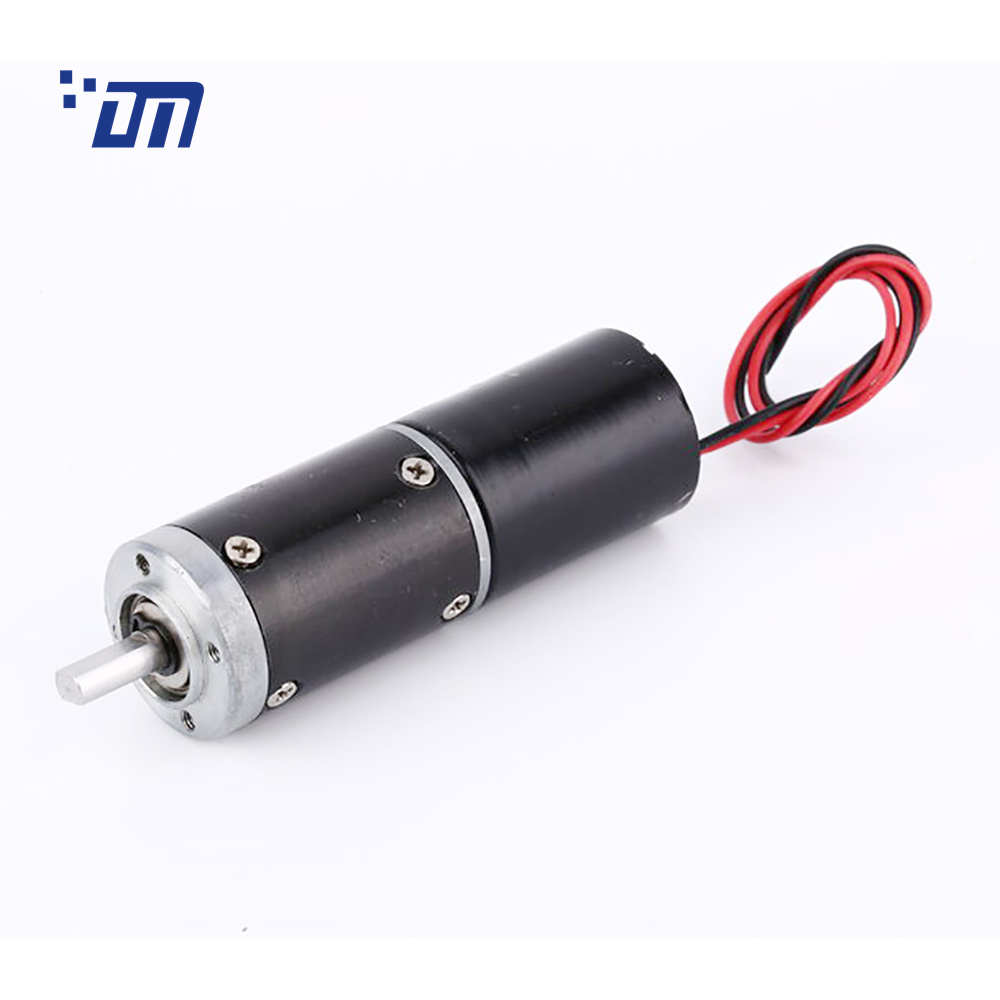
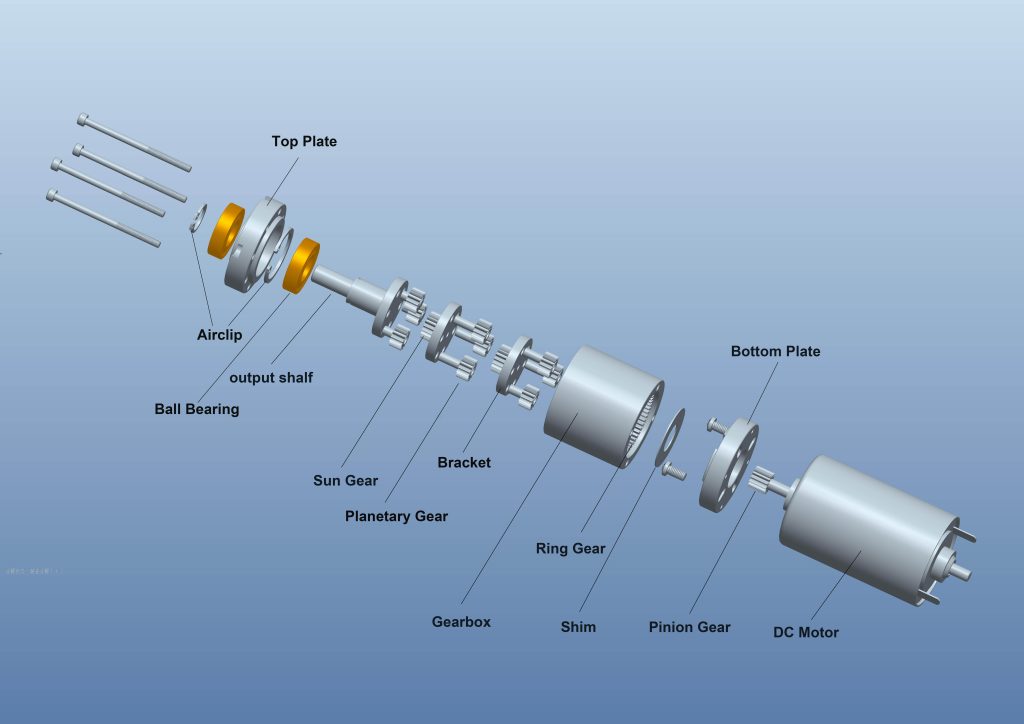
DC Gear Motor
DC Gear Motor is DC motor connect with gearbox. In a DC motor, the shaft connects the first stage gear and the gearbox’s first gear. As the DC motor operates, it drives the gears, resulting in the rotation of the output shaft.
The rotational power generated by the motor is transmitted through the gear system, allowing for controlled and efficient rotation of the output shaft.
This mechanism enables the DC motor to convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, making it a versatile and widely used component in various applications.

DC Gear Motor
Benefits of DC gear motor
- High Torque, High Detent Torque, High RPM, Low Noise, Small Backlash, High Precision
- Durable and High efficiency, Small Cogging Torque
- Compact size, Customized Shaft direction
- High Durability, Waterproof, Long Lifespan
- Higher Speed Range, buit-in Driver
Why Choose DONGMING MOTOR
Innovative R&D Engineering for Your Project
- Considering the rationality and convenience of the production process from the design stage.
- If our existing “standard” DC gear motor cannot provide the optimal performance, we R&D team will work with you to develop customized DC gear motor solution.
Modernized High Volume Manufacturing
4+ semi-automatic production lines, 2400000PCS DC gear motors/month
Quality & Reliability Policy
- Considering the rationality and convenience of the production process from the design stage
- Adopting the international advanced quality management system, strict management of IQC, production and QA
Effective Communication and Collaboration
- Customer needs analysis team respond to customer quickly and professionally
- Professional sale engineers provide one-stop customized services
Professional R&D engineer team work for you
From developing&research, prototype, testing, small batch test, mass production and after-sales service
Start the DC Gear Motor Custom Service for Your Project

Requirements discussion
To ensure providing the best solution of DC gear motor, the sales engineers should discuss with customer some important infomation including:
- The installation dimension for DC gear motor
- The parameter for DC gear motor includes operation load speed, operation load torque, voltage, output load current,stall torque, stall current, work cycle, working condition, noise level, lifetime,Electromagnetic shielding, etc
- The certification requirements, such as CE, ROHS, SGS, TEACH.
- The target cost and project plan.
Project Evaluation
According customer’s requirments for DC gear motor and other information of project, our R&D team analyst and evaluate the project. And to confirm provide our exsiting solution or build a new solution. If to design a new DC gear motor, DONGMING design team will provide the project evaluation report for the development time, mold cost and risk.


Prototype sample manufacturing
To confirm all requirements with customers step by step, our R&D will utilize the design software to design a product or set a 2D/3D drawing for DC gear motor.
Sample performance test
When the sample is completed, our R&D team will test the DC gear motor’s all performance with our precise test equipment. If customers have lifetime requirement, we will provide the lifetime cycle test in laboratory.


Small batch production and mass production
Start a trial production after sample working perfectly on product. Launch small batch to test customers’ market.
Finally start the mass production
We have the compeleted quality control system for production.
Delivery and after-sales service
When products ready to ship, we are also responding for logistics to make sure customer picks up all products satisfied.
If customers have any issue after sales, our team will support to solve it always.

DC Motor Types
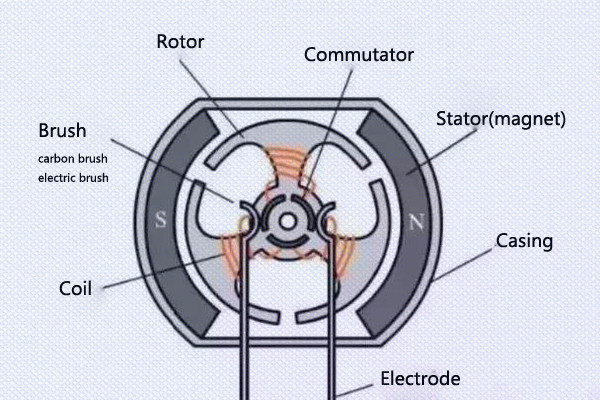
Brushed DC Motor
Brushed DC motors work by having the coil rotate inside the surrounding magnets. The rotation of the coil causes the contact between commutator and brush to alternate, therefore switching the current flow through the coil. As a result, the brushed DC motor can operate.
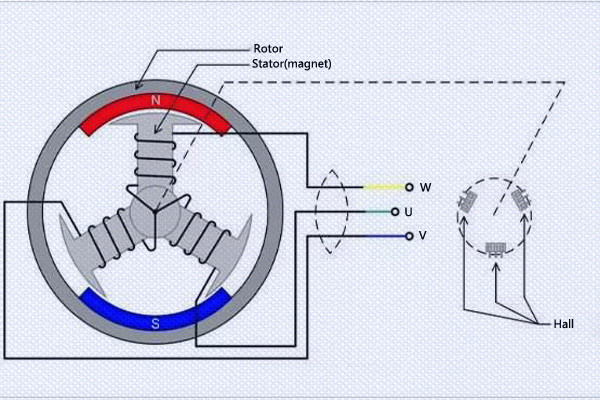
Brushless DC Motor
A Brushless DC Motor (BLDC) is an electric motor powered by a direct current voltage supply and commutated electronically instead of by brushes like in conventional DC motors. BLDC motors are more popular than the conventional DC motors nowadays, but the development of these type of motors has only been possible since the 1960s when semiconductor electronics were developed.
Gearbox Types
Spur Gearbox
Spur gears are used in mechanical applications to increase or decrease the speed of a device or multiply torque by transmitting motion and power from one shaft to another through a series of mated gears.Spur gears are more efficient compared to helical gears with the same size. They are quite reliable and offer constant velocity. Spur gears are also considered a member of positive transmission because they don't have any slippage
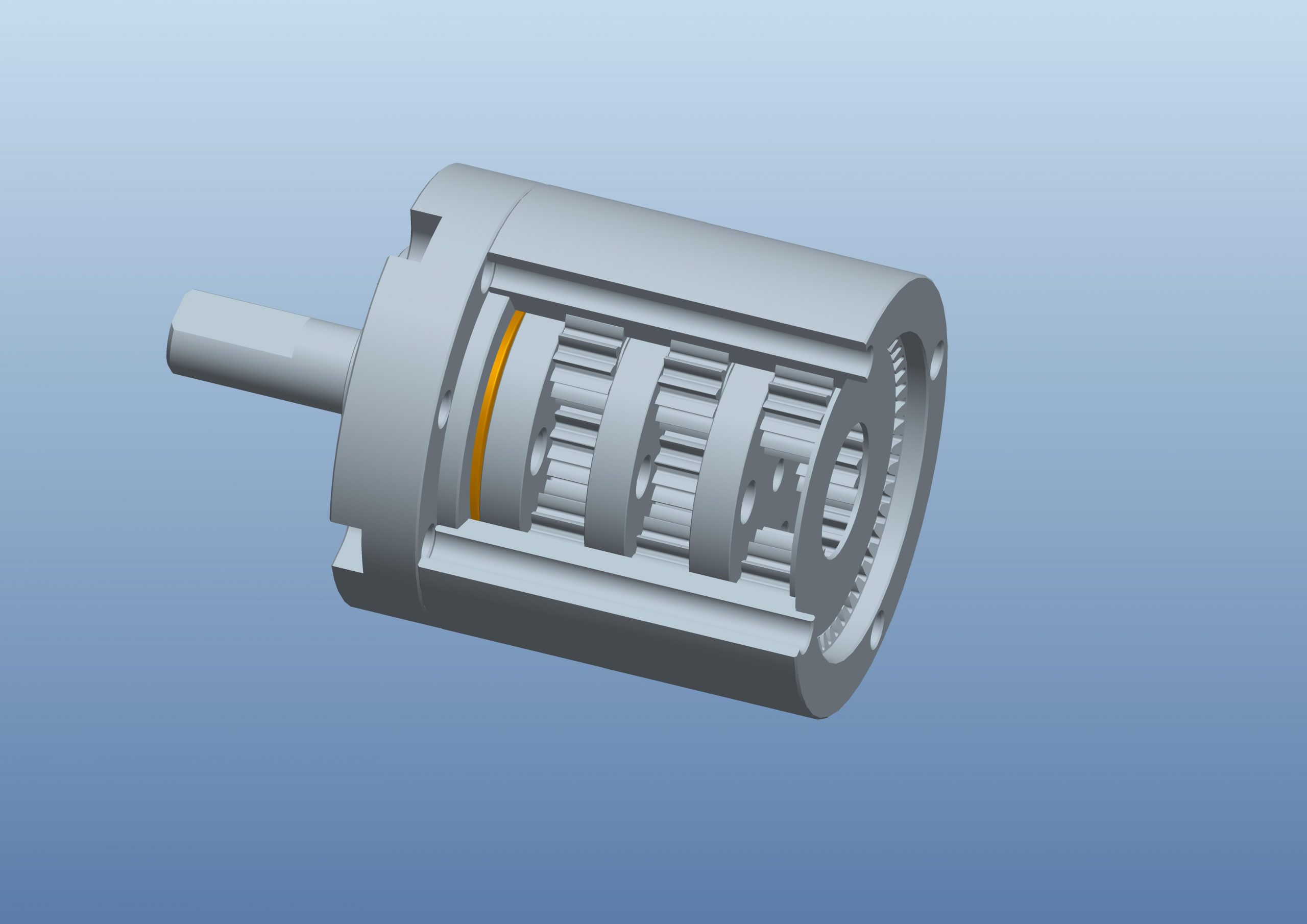
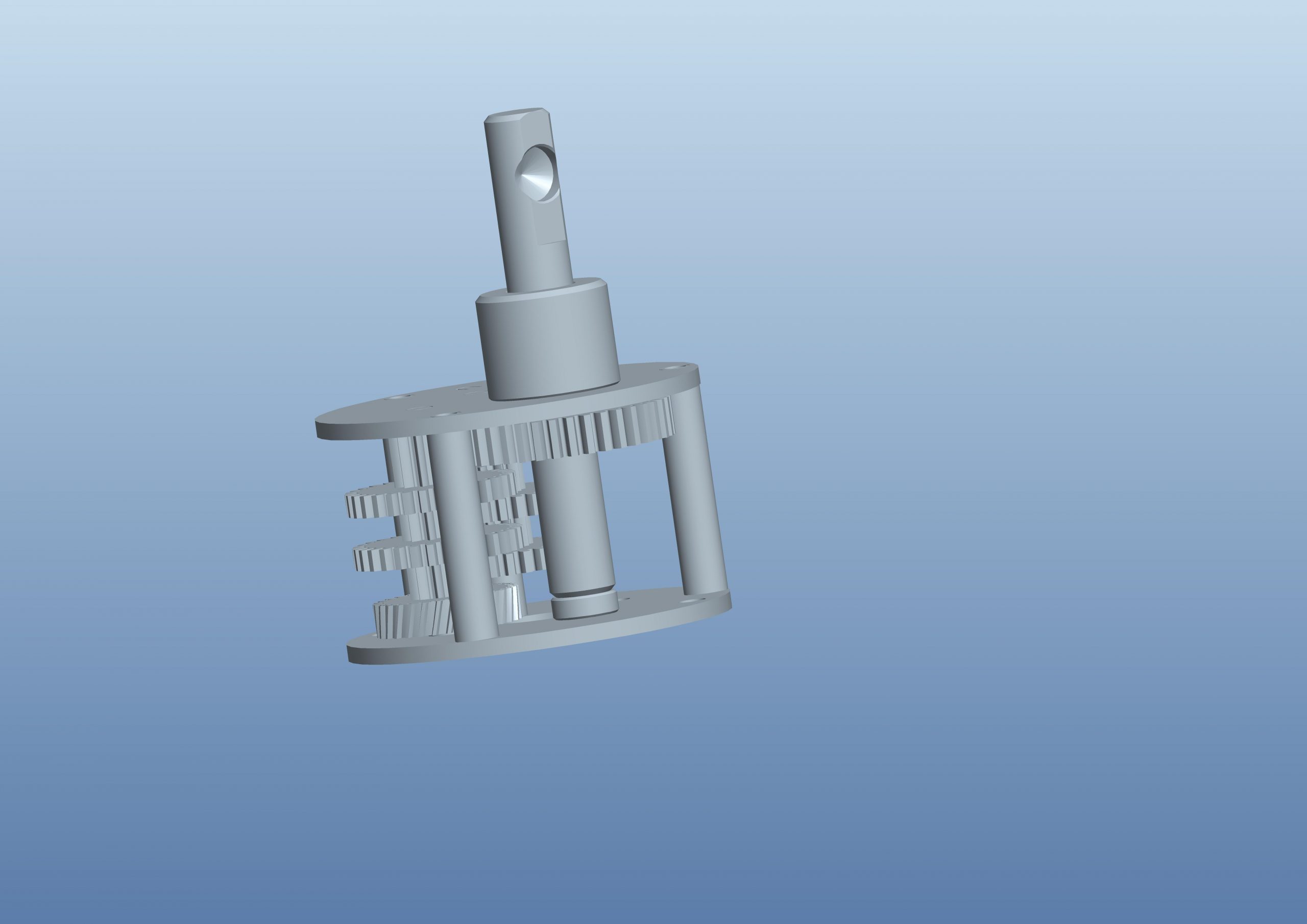
Planetary Gearbox
A planetary gearbox is a gearbox with the input shaft and the output shaft aligned. A planetary gearbox is used to transfer the largest torque in the most compact form (known as torque density).Planetary gear systems are able to produce a lot of torque because the load is shared among multiple planet gears. This arrangement also creates more contact surfaces and a larger contact area between the gears than a traditional parallel axis gear system.
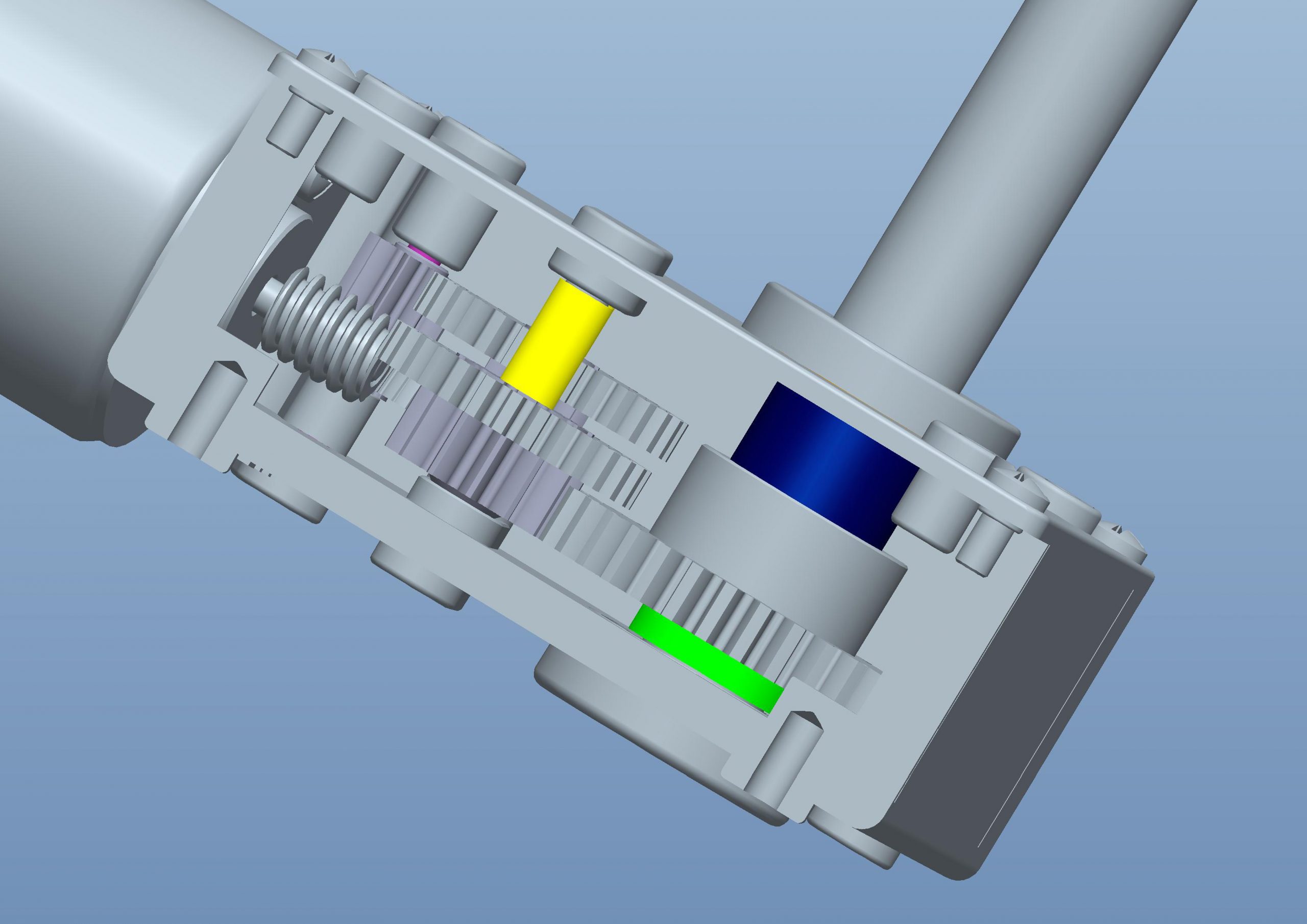
Worm Gearbox
Worm gears operate by the friction created by turning lubricated gears. The friction is then converted into heat. By producing a low speed and high-speed torque level, worm gears are utilised as speed reducers, which implies that they are ideal for several applications. In theory, a worm gear is self-locking when the static friction angle is larger than the helix angle of the worm. The static friction angle is described as the angle where the load above will start to move.
DC Gear Motor Applications

Robotics
From robotic arms to teaching robotics and robotic toys, flat gear motors play a crucial role in facilitating precise and controlled movements.

Sanitary Automations
In dispensers, lid openers, and sensor sanitary bins, flat gear motors contribute to the seamless functioning of sanitary automation systems.

Safe and Security Systems
Electronic locks, door locks, safes, and latch closers benefit from the reliability and efficiency of flat gear motors.

Valve/Meter Mechanisms
Electric valves, gas meters, and water meters leverage flat gear motors for optimal performance.

Curtain Automation
Electric curtains and blinds are enhanced with the controlled and efficient movement provided by flat gear motors.

Coffee Machines
In the realm of coffee machines, including coffee makers and bean grinders, flat gear motors ensure precise and reliable operations.
Pet Care Devices
From anti-bark devices to pet feeders and door openers, flat gear motors contribute to the comfort and well-being of our furry friends.

Bank Automation
ATMs, coin counters, coin selectors, coin validators, and banknote counters benefit from the precision and durability of flat gear motors.

Vending Machines
Beverage vending machines, hot and cold drink dispensers, and juicer makers rely on the efficiency and reliability of flat gear motors.
Medical Care Equipment
Diagnostic equipment, medical beds, massagers, and beauty care appliances are empowered by the precision movements of flat gear motors.

Others
From BBQs and 3D printing to baby cradles, fish feeders, humidifiers, and range hoods, flat gear motors find applications in a diverse array of industries and products.
DC Gear Motor Guide
Looking for information about DC gear motors? Learn how these motors operate, their working principles, and the differences between DC gear motors and DC motors. Discover why DC gear motors can overheat and even burn out, including factors such as current, speed, and long-time running. Find out how to prevent burnout and extend the lifespan of your DC gear motor. Get answers to all your questions about DC gear motors and more.
How the DC gear motor operates?
The versatility to produce high torque at low speeds makes the DC gear motors suitable for various applications. It would be great to consider the mode of operation and factors that affect the performance of such devices.
In a DC motor, the shaft connects the first stage gear and the gearbox’s first gear. As the DC motor operates, it drives the gears, resulting in the rotation of the output shaft. The rotational power generated by the motor is transmitted through the gear system, allowing for controlled and efficient rotation of the output shaft. This mechanism enables the DC motor to convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, making it a versatile and widely used component in various applications.
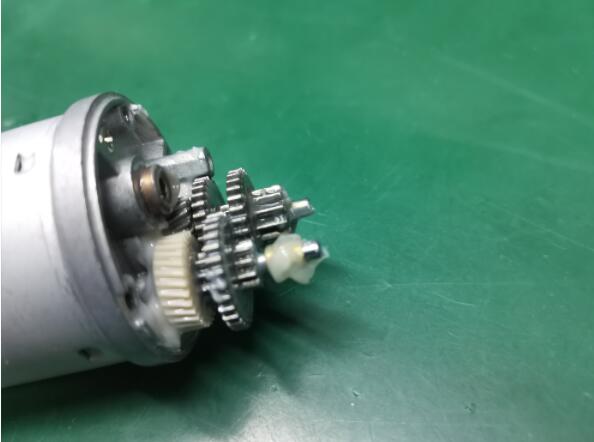

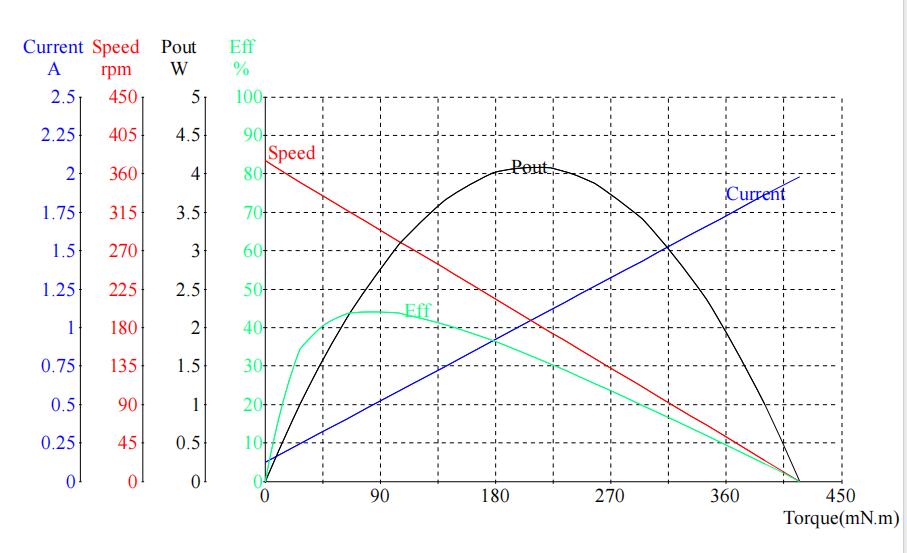
The rated torque is the torque that the motor can deliver continuously. In contrast, the max efficiency torque is the maximum torque the motor can deliver when the output shaft is prevented from rotating. Additionally, the voltage and current supplied to the motor can affect its performance, so selecting a motor that can handle the required voltage and current for your application is crucial.
DC gear motor: Understanding the working principle.
The motor comprises a stator, rotor, and commutator. The stator houses electromagnets, the rotor contains permanent magnets, and the commutator is the copper segment. The primary component that enhances the efficiency, i.e., using less energy to generate higher torque of this motor, is the gearbox attached to the output shaft. This energy can power other devices, making DC gear motors versatile and widely used in various applications.
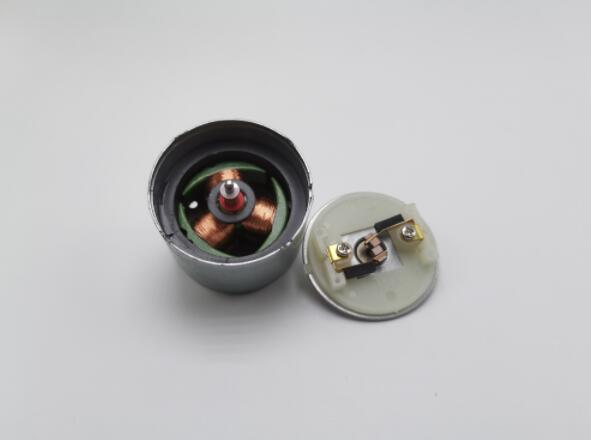

The performance of a DC gear motor is determined by several factors, including the motor’s rated torque and stall torque, the voltage and current supplied to the motor, and the design and quality of the gearbox. By selecting the suitable motor and gearbox combination for the application, users can optimize the efficiency and performance of their DC gear motor. By understanding the essential components and their functions, users can select the right DC gear motor for their specific application and achieve optimal performance and efficiency.
What are the differences between a DC gear motor and a DC motor?
If you’re in the market for a motor, you’ve likely come across DC motors and DC gear motors. They typically consist of a rotor (the rotating component of the motor), a stator (the stationary structure), and a commutator (a set of copper segments that conduct electricity to the electromagnets in the stator). Both types of motors are commonly used in various applications, but they have some distinct differences to be considered in the following paragraphs.
DC motors and DC gear motors differ in their torque output and speed. The gearbox in a DC gear motor increases the torque output of the motor while reducing its speed, making it suitable for devices that require precise speed, such as robotics and other smart home equipment.
Other factors to consider when choosing between DC motors and DC gear motors include the output shaft, rated torque, stall torque, current, voltage, and gearbox ratio. DC gear motors are typically available in various sizes and gear ratios to suit various applications, while DC motors are more precise in selecting various applications.
In summary, the main differences between DC gear motors and DC motors are the presence of a gearbox and the resulting differences in torque and speed.
What are the reasons for a DC gear motor to overheat?
If you are using a DC gear motor, you may have experienced overheating at some point. Let’s use the following paragraphs to examine the factors that could result in overheating and the various prevention.
One of the most common reasons a DC gear motor overheats is excessive current. You can expect a breakdown if the motor works at a higher current rate than the manufacturer’s specifications. Another reason for overheating can be due to the motor’s speed. This is often brought on by things like utilizing the incorrect gear ratio or having a broken controller.
Another cause of overheating in a DC gear motor is stalling. Stalling in a DC gear motor refers to the condition where the motor stops rotating despite having sufficient voltage applied to its terminals. This occurs when the torque demand from the load exceeds the maximum torque (known as the breakdown torque) that the motor can generate. When a force is applied to stop the output shaft while power is supplied to the DC gear motor, it enters a stall state. In this condition, the motor draws the maximum current, dropping its speed to zero.
Stalling can happen for various reasons, such as when the load becomes too heavy or encounters an obstruction. It can also occur if the motor is overloaded beyond its specified capacity. When the motor stalls, it cannot deliver the required rotational force to overcome the resistance, resulting in a complete halt in its motion.
When a motor stalls, it experiences a prolonged duration of high current draw, which can cause excessive heat buildup in the motor’s windings and components. This overheating can have detrimental effects on the motor’s performance, potentially leading to insulation damage, reduced efficiency, and even motor failure. Therefore, it is crucial to prevent stalling and subsequent overheating by adequately sizing the motor for the load and ensuring it operates within its specified limits. Implementing protective measures such as overload protection devices or employing thermal management techniques like cooling fans or heat sinks can also help mitigate the risk of overheating in DC gear motors.
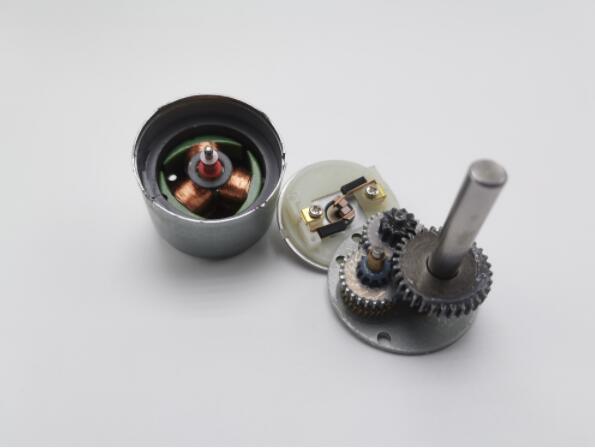

The long-term operation of a DC gear motor can cause overheating, which could damage parts of the motor. If the motor is operated continuously for extended periods, it can cause the motor to generate excessive heat, leading to overheating. This can be caused by insufficient cooling or using the motor beyond its rated duty cycle.
To prevent overheating, it is essential to ensure that the motor is operated within its rated limits, using the correct power supply and voltage, and having an appropriate gear ratio. Monitoring the motor’s temperature during operation and implementing appropriate cooling mechanisms such as fans or heatsinks is also essential.
In conclusion, a DC gear motor can overheat for various reasons, such as excessive current, speed, stall torque, long-term operation, etc. By understanding the causes and taking appropriate measures to prevent overheating, you can ensure optimal performance and prolong the lifespan of your DC gear motor.
What causes a DC gear motor to burn out?
A DC gear motor is susceptible to damage and failure, including burnout. Burnout occurs when the motor is subjected to excessive heat or current, damaging or destroying the motor’s components. Let’s discuss the common causes of DC gear motor burnout and how to prevent it.
One of the primary causes of DC gear motor burnout is overloading. When the motor is subjected to excessive loads beyond its rated torque, it can cause the motor to overheat and eventually burn out. Therefore, ensuring that the motor is not overloaded and that the application’s requirements are within the motor’s rated torque is essential.
Another cause of DC gear motor burnout is improper wiring. Suppose the motor is wired incorrectly or the voltage and current supplied to the motor are not within the manufacturer’s specifications. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure that the motor is wired correctly and that the voltage and current are within the specified range.

The condition of the motor’s gearbox can also contribute to burnout. If the gearbox is not properly lubricated, damaged, or worn, it can cause the motor to overheat and eventually fail. Therefore, ensuring that the gearbox is appropriately maintained and that the motor is operated within the recommended operating conditions.
In conclusion, DC gear motor burnout can be caused by overloading, improper wiring, gearbox condition, and environmental factors. By taking appropriate measures, such as ensuring proper loading, wiring, gearbox maintenance, and operating conditions, users can prevent burnout and extend the lifespan of their DC gear motor.





